Follistatin 344 and The Life Cycle

All animal test participants’ tissues express Follistatin 344, an autocrine glycoprotein. Activin-binding protein (FST) or Activin-binding protein There are 36KDa of it in weight, and its molecular formula is C13H16O3.
Follistatin’s Operational Mechanisms
TGF- superfamily members are the primary target of Follistatin 344, which has been shown to bind and neutralize the components. According to the research, the peptide exhibits a strong affinity for activin, a protein complex involved in producing and releasing stimulating follicle hormone. FSH production and secretion are inhibited by Follistatin 344, which binds directly to activin and functions specifically as an activin antagonist (FSH)
Follistatin 344’s overall functioning originates in the anterior pituitary gland’s solliculostellate (FS) cells. Several endocrine-related processes in the body of an animal test subject are controlled and regulated by this pea-sized gland situated at the base of the hypothalamus in the brain.
Cells are linked to Follistatin 344 because they have an essential function in regulating cell proliferation. Follistatin 344 is a cellular growth inhibitor that has been tested on animals. Cellular differentiation occurs when an unspecialized cell unit is transformed into a more specialized cell type using peptides, which function as an instrument of cellular differentiation. Both of these activities are critical in developing and repairing new tissue in scientific studies using animals. This finding has prompted some investigations to assume that the peptide’s increased skin presence is associated with this specific functioning feature.
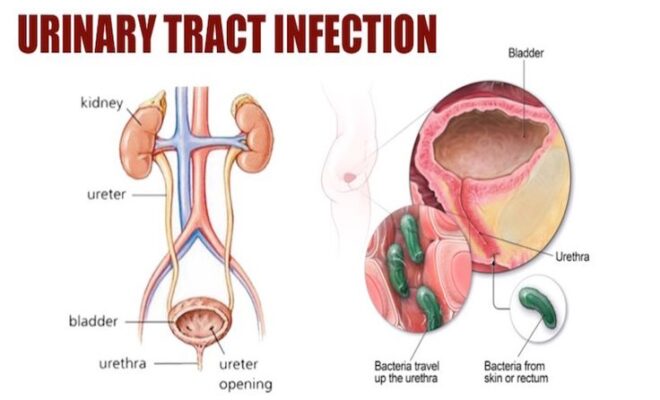
Follistatin 344 has also been shown to function in the blood of animal test participants, as discovered via scientific investigation. Furthermore, its presence may provoke an inflammatory reaction, the body’s complicated biological response to potentially hazardous stimuli, such as infections and damaged cells. However, due to its autocrine feature, it has been postulated that it may originate from endothelial cells, the thin layer of cells that line the inner surface of blood arteries, in circulating blood plasma. The white blood cells known as monocytes and macrophages may be the peptide source.
The Life Cycle and Follistatin 344
The peptide has also been shown to function in the development of embryos in animal investigations. Bone-morphogenic proteins, which are essential for forming the neural plate, may be inhibited by the presence of the peptide.
Further research has shown that the peptide aids folliculogenesis in the ovaries of female animal test participants, which means that its presence promotes follicle maturation and preparation for reproduction. Researchers working with animal test subjects believe that this peptide is crucial in fostering follicular development. This is the case, particularly in moving the cells that make estrogen into the antral/dominant stage and promoting the differentiation of estrogen-producing granulose cells into progesterone-producing large lutein cells. The fact that the female ovary has the most significant number of FS cells generated by the anterior pituitary gland explains why the peptide has been linked to the ovaries.
Some studies have investigated the possible link between Follistatin 344 and polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), also known as hyperandrogenic anovulation or Stein-Leventhal syndrome, because of how the peptide works the ovaries of female animal test subjects. It is considered that this specific endocrine abnormality, which is frequent in female animal test subjects, is a significant contributor to female infertility. According to some research, the development of the disease might be caused by a mutation in this specific peptide. Nevertheless, more research is needed to determine the peptide’s precise function in the onset of polycystic ovarian syndrome. If you are a researcher, you can buy Follistatin-344 online for research purposes only.